Why POF Shrink Film Is Becoming the Go-To Packaging Solution for Modern Manufacturers
Jan 27,2026POF Film Explained: Performance Advantages, Application Scenarios, and Buying Considerations for Modern Packaging
Jan 21,2026Is Your Production Line Ready for High-speed Packaging Polyolefin Shrink Film?
Jan 14,2026Why is Shading Cross-Linked Shrink Film Revolutionizing the Protection of Light-Sensitive Products?
Jan 06,2026The Ultimate Guide to Cross-Linked Shrink Film: Why It’s the Gold Standard for Modern Packaging
Jan 04,2026Polyolefin (POF) shrink wrap film is widely used in packaging due to its excellent clarity, strong seal strength, and environmentally friendly properties. It is a preferred choice for wrapping food, electronics, toys, cosmetics, and many other consumer goods. Understanding how POF shrink wrap film is produced can provide valuable insight into its high-performance characteristics and widespread application. Below is a detailed step-by-step overview of the production process of POF shrink wrap film.
1. Raw Material Selection
The primary raw materials used in POF shrink film production are polyolefins, usually a combination of:
Low-Density Polyethylene (LDPE)
Linear Low-Density Polyethylene (LLDPE)
Polypropylene (PP)
These resins are selected for their flexibility, clarity, and ability to form a stable multilayer structure when co-extruded. Additives such as slip agents, anti-block agents, and processing aids may also be included to enhance the film’s functionality.
2. Extrusion Process
POF shrink film is typically made using a five-layer co-extrusion process, which combines different resins to achieve optimal performance. The key stages include:
Feeding and Melting: The selected polymers are fed into separate extruders and melted at high temperatures (around 200–250°C).
Co-extrusion Die: The molten polymers are simultaneously forced through a specialized die head that creates a five-layer film structure. Each layer contributes specific properties such as strength, flexibility, and sealing ability.
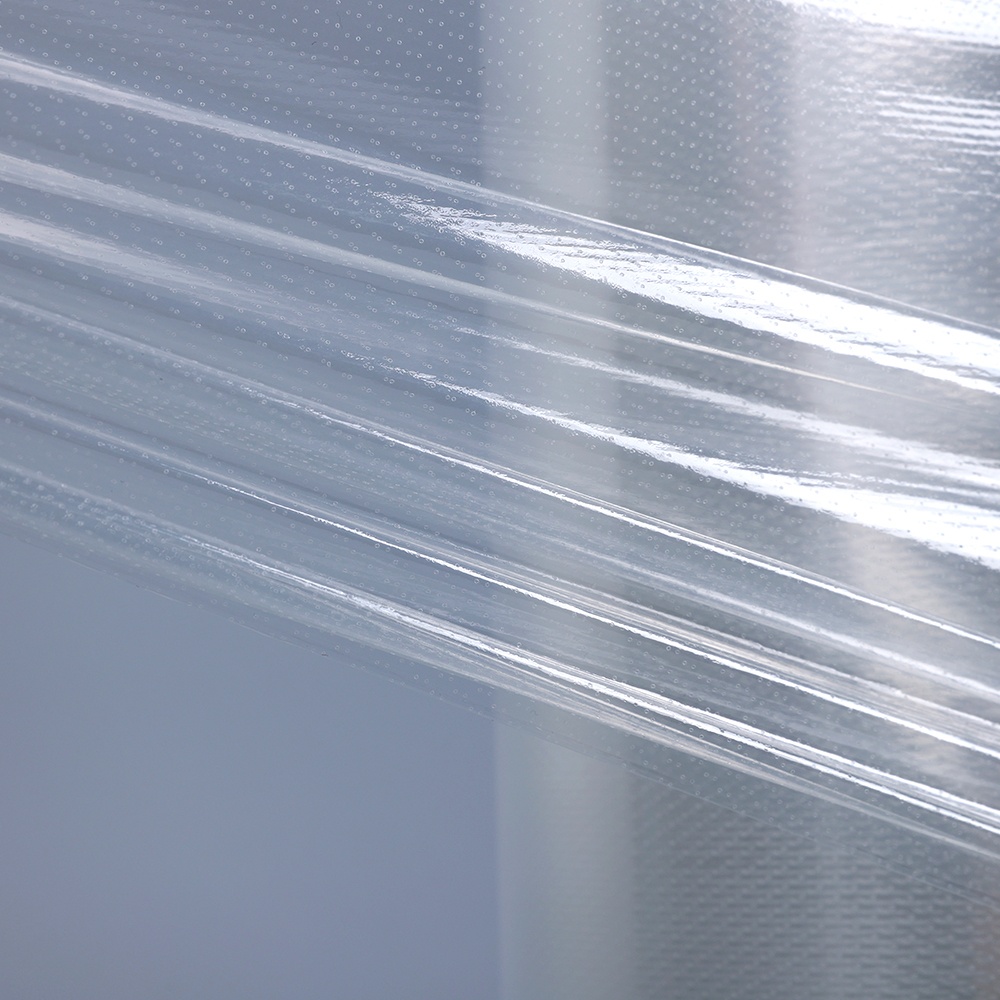

3. Bubble Blowing or Water Quenching
There are two common production methods after co-extrusion:
Blown Film Method: The film is extruded in a bubble form and blown upward with air pressure. The bubble is cooled gradually with air rings and then collapsed to form flat film.
Water Quenching Method: The hot extruded film is rapidly cooled using water baths or chill rollers, which improves film clarity and smoothness.
Each method affects the film’s optical properties and shrink performance. Blown film is more common for thicker films, while water quenching is ideal for high-clarity films.
4. Orientation (Stretching)
To give the film its shrinkable properties, it undergoes biaxial orientation:
Machine Direction (MD): The film is stretched longitudinally by passing through a series of rollers at increasing speeds.
Transverse Direction (TD): The film is then stretched horizontally using a tenter frame system or bubble inflation.
This stretching aligns the polymer chains, giving the film its ability to shrink uniformly when heated during packaging.
5. Annealing and Heat Setting
After orientation, the film is heat-treated to stabilize its properties and reduce internal stress. This step improves:
Shrink consistency
Dimensional stability
Sealing performance
6. Slitting and Winding
The finished film is slit into desired widths based on customer requirements. It is then wound into rolls using high-speed winding machines, ensuring uniform tension and smooth roll edges.
7. Quality Inspection and Packaging
Every roll is inspected for:
Clarity
Thickness uniformity
Shrink rate (typically 60–70% in TD and 20–30% in MD)
Seal strength
Defective rolls are rejected or reprocessed. Approved rolls are packed in protective film or cartons for shipping.
Understanding POF Shrink Film: A Versatile Packaging Solution
What To Consider When Buying Polyolefin Shrink Film?
Mobile site

alibaba
Copyright © 2023 Zhejiang Zhongcheng Packing Material Co., Ltd. All Rights Reserved. Privacy Polyolefin Shrink Film Manufacturers